In this post we're going to run the same tests we ran in our previous post; however, these tests will be done with POCO (Plain Old CLR Object) classes in place.
We're going to perform the following:
- Rearrange solution project and files.
- Create POCO Classes.
- Create ObjectContext.
- Run CRUD operations and Performance test.
- Compare results of auto generated Entities against POCO classes.
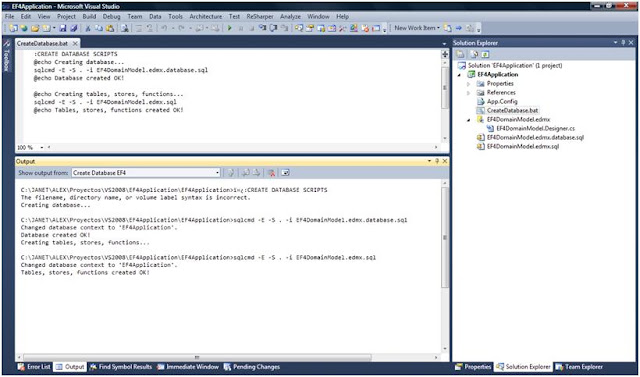
Let's start by changing the file arrangements in our solution. Let's add two class library projects: one to keep the database scripts and batch file and another named EFApplicationWithPOCO for the POCO Classes and Context.

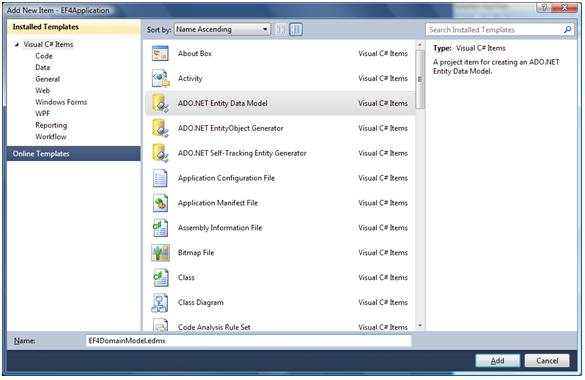
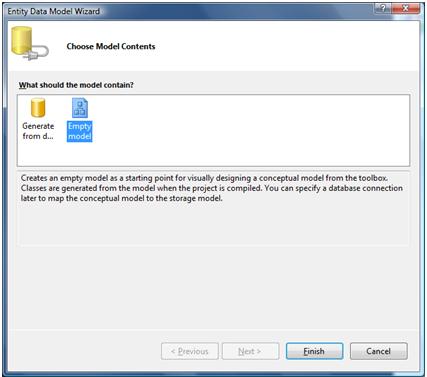
Add a new ADO.NET Entity Data Model by using the Update Model From Database wizard to generate the model.
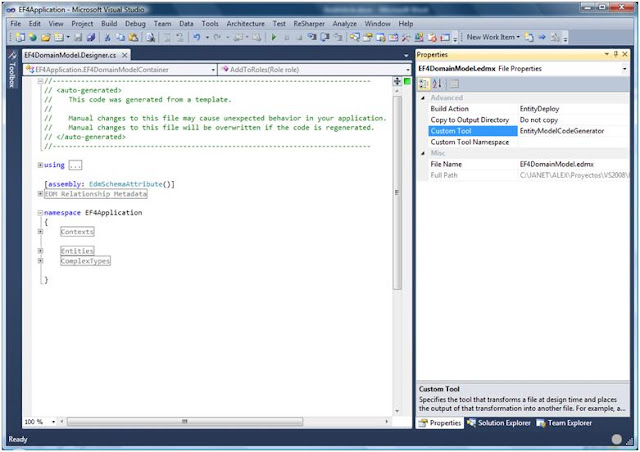
Empty the Custom Tool property of the Edmx file. This will remove the EF4DomainModelForPOCO.Designer.cs auto generated file and it won't generated again.
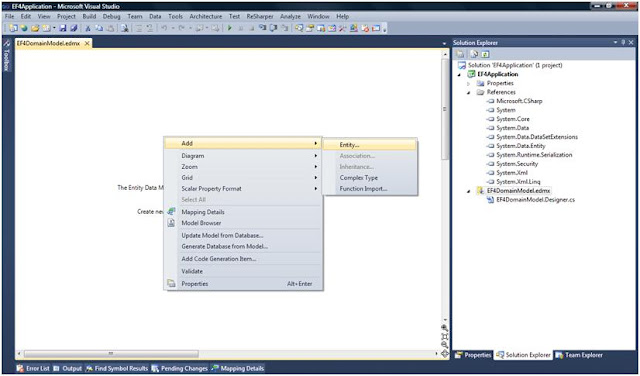
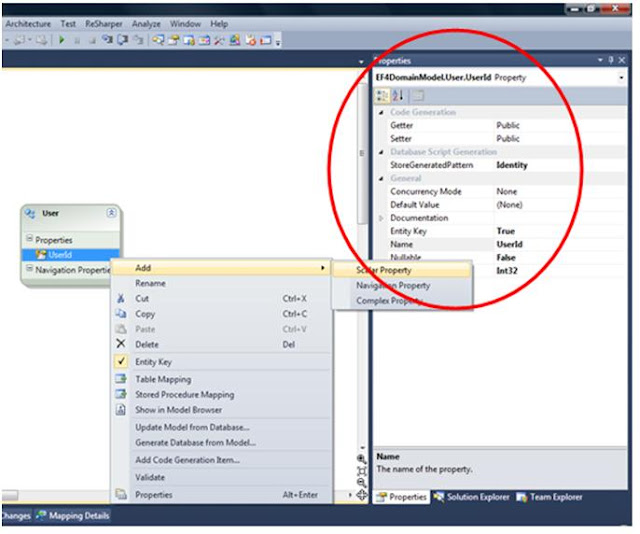
Write your POCO and ObjectContext classes.
Role.cs
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace EF4ApplicationWithPOCO { public class Role { public Int32 RoleId { get; set; } public String RoleName { get; set; } public virtual List<User> Users { get; set; } } }User.cs
using System; namespace EF4ApplicationWithPOCO { public class User { public Int32 UserId { get; set; } public String UserName { get; set; } public String FirstName { get; set; } public String LastName { get; set; } public DateTime? DateOfBirth { get; set; } public Int32 RoleId { get; set; } public virtual Role Role { get; set; } } } EF4ApplicationPOCOContext.cs
using System.Data.Objects; namespace EF4ApplicationWithPOCO { public class EF4ApplicationPOCOContext : ObjectContext { public EF4ApplicationPOCOContext() : base("name=EF4DomainModelContainerForPOCO", "EF4DomainModelContainerForPOCO") { ContextOptions.LazyLoadingEnabled = true; } private ObjectSet<User> _users; public ObjectSet<User> Users { get { if (_users == null) _users = CreateObjectSet<User>("Users"); return _users; } } private ObjectSet<Role> _roles; public ObjectSet<Role> Roles { get { if (_roles == null) _roles = CreateObjectSet<Role>("Roles"); return _roles; } } public void AddToRoles(Role role) { Roles.AddObject(role); } public void AddToUsers(User user) { Users.AddObject(user); } } }
Now that we've created our POCO and ObjectContext classes, we can add code to the TestCrudeOperationsWithPOCO.cs class and implement it as follows.
using System; using System.Linq; using EF4ApplicationInterfaces; namespace EF4ApplicationWithPOCO.Temp { public class TestCrudeOperationsWithPOCO : IEF4ApplicationTest { public void CreateDbTest() { using (var context = new EF4ApplicationPOCOContext()) { Console.WriteLine("INSERTING ROLES TO DATABASE"); context.AddToRoles(new Role {RoleName = "Role 1"}); context.AddToRoles(new Role {RoleName = "Role 2"}); context.AddToRoles(new Role {RoleName = "Role 3"}); context.SaveChanges(); Console.WriteLine("INSERTING USERS TO DATABASE"); var firstRole = context.Roles.Where(t => t.RoleName == "Role 1").FirstOrDefault(); context.AddToUsers( new User { UserName = "user1", FirstName = "FirstName1", LastName = "LastName1", DateOfBirth = new DateTime(1980, 12, 10), Role = firstRole }); var secondRole = context.Roles.Where(t => t.RoleName == "Role 2").FirstOrDefault(); context.AddToUsers( new User { UserName = "user2", FirstName = "FirstName2", LastName = "LastName2", DateOfBirth = new DateTime(1980, 12, 11), Role = secondRole }); var thridRole = context.Roles.Where(t => t.RoleName == "Role 3").FirstOrDefault(); context.AddToUsers( new User { UserName = "user3", FirstName = "FirstName3", LastName = "LastName3", DateOfBirth = null, Role = thridRole }); context.SaveChanges(); } } public void UpdateDbTest() { using (var context = new EF4ApplicationPOCOContext()) { Console.WriteLine("UPDATING USER INFORMATION"); var user1 = context.Users.Where(t => t.UserName == "user1").FirstOrDefault(); user1.FirstName = "Alexandro"; user1.LastName = "Velarde"; context.SaveChanges(); } } public void ReadFromDbTest() { using (var context = new EF4ApplicationPOCOContext()) { Console.WriteLine("VIEW INSERTED USERS"); var users = context.Users; foreach (var u in users) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format( "UserName = {0}, FirstName = {1}, LastName = {2}, DateOfBirth = {3}", u.UserName, u.FirstName, u.LastName, u.DateOfBirth.HasValue ? u.DateOfBirth.Value.ToString("MM/dd/yyyy") : string.Empty)); } } } public void PerformanceTest() { using (var context = new EF4ApplicationPOCOContext()) { var users = context.Users; Console.WriteLine("PERFORMANCE TEST STARTED..."); var user = users.FirstOrDefault(); string readValueOneMillionTimes = null; var timeWhenTestStarted = DateTime.Now; for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) readValueOneMillionTimes = user.Role.RoleName; var duration = DateTime.Now.Subtract(timeWhenTestStarted); Console.WriteLine("VALUE READ: " + readValueOneMillionTimes + " DURATION: " + duration.TotalMilliseconds + " MILLISECONDS"); Console.WriteLine("PERFORMANCE TEST END"); } } public void DeleteFromDbTest() { using (var context = new EF4ApplicationPOCOContext()) { Console.WriteLine("DELETE USERS FROM DATABASE"); foreach (var userToDelete in context.Users) context.DeleteObject(userToDelete); foreach (var role in context.Roles) context.DeleteObject(role); context.SaveChanges(); } } public void RunAllTest() { CreateDbTest(); Console.WriteLine(); UpdateDbTest(); Console.WriteLine(); ReadFromDbTest(); Console.WriteLine(); PerformanceTest(); Console.WriteLine(); DeleteFromDbTest(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
Now let's RUN our the performance test for both projects and COMPARE the results.
Program.cs
using System; using EF4Application.Temp; using EF4ApplicationWithPOCO.Temp; namespace EF4ConsoleApplication { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("====== RUNNING AUTO GENERATED CLASSES ======"); new TestCrudeOperationsNoPOCO().RunAllTest(); Console.WriteLine("====== RUNNING POCO CLASSES TEST ======="); new TestCrudeOperationsWithPOCO().RunAllTest(); } } }
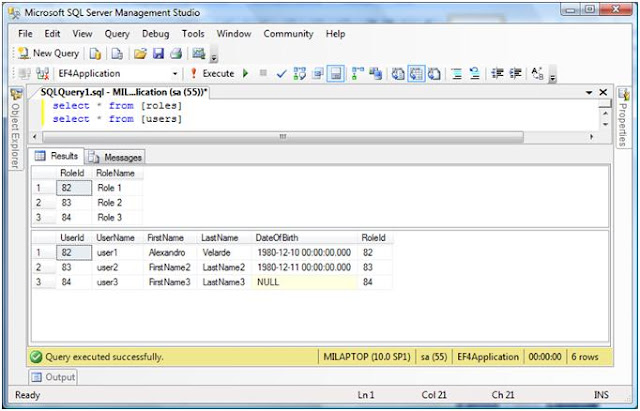
Here are the results. Look at the huge difference between POCO and auto generated entities.
Summary
I think there should be more performance test to be done, but thisone gives you a good idea on where to focus.
What's next?
In the next post, I can enhance the performance test with much more complex cases to measure the POCO performance for tracking. After we can see how to write templates to auto generate POCO classes or any good idea you can come up with... Let me know!.
I hope this was useful, thanks for reading..